Macular Degeneration
I. What is Retina and Macula
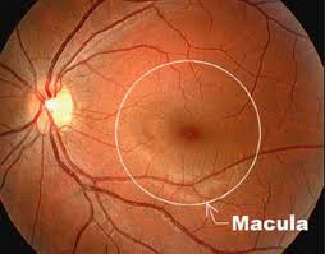
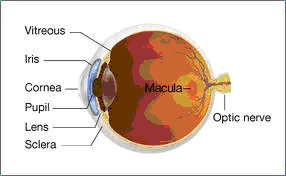
The retina is a thin layer of neural tissue lining the back inner surface of the eye. The macula is the small, central portion of the retina( Fig.1, 2 )
 |
 |
|
| Fig. 1. Retina photo showing macula (from Google Images) |
Fig.2. Cut eyeball showing macula on the back |
II. What is macular degeneration (MD)?
MD is a degenerative disease o f macula where there are atrophy or apoptosis of the light-sensitive cells ( rods and cones) and/or drusens under the retina , called dry macular degeneration. With progress of the disease, new blood vessels and bleeding appear and it is referred to as wet macular degeneration.
III.Classifications of MD
According to the pathogenesis, there are three types of MD:- 1. Age-related MD (AMD);
-
2. Myopic MD (MMD);
- 3. Juvenile macular degeneration or Stargardt’s disease.
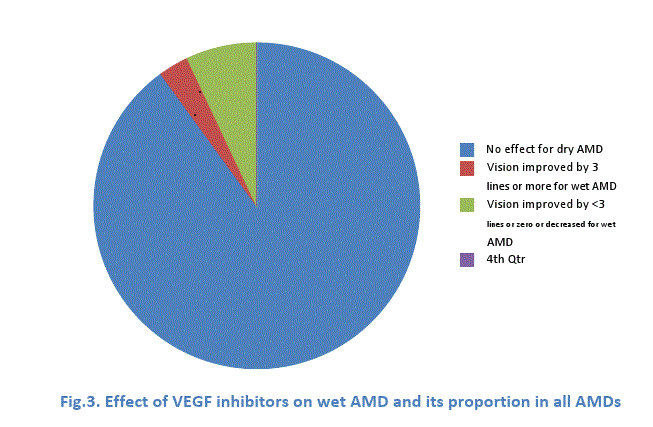
- 1.Wet AMD accounts for 10 % of all AMDs,
- 2. Dry AMD, 90%
IV Symptoms of MD:
 |
 |
|
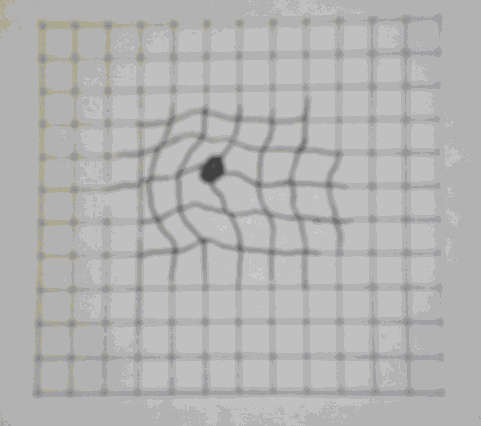
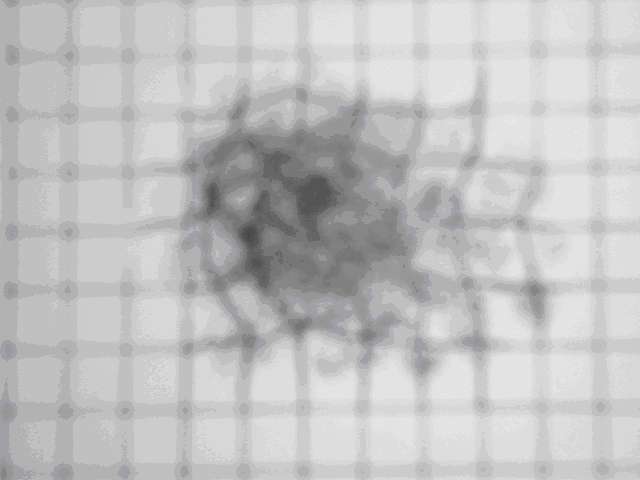
| 1.Visual distorion | 2.Dark cloud in central visual field |
V.Treatment of MD
An ideal treatment should be able to take care of all the controllable contributing factors, all the pathologic changes and with minimum side effects.
A. Western medicine treatments:
For a long time, the Western medicine treatments have focused on the new blood vessels which is only one of the 7 pathologic changes related to this eye disease.
1. Laser photocoagulation: This treatment uses hot laser radiation to coagulate retinal new blood vessels around macula and stop bleeding, but this procedure causes damage to the normal retina, leading to scar tissue and permanent visual impairment. Moreover, it does not prevent the new blood vessels from forming again.
2. Photodynamic therapy(PDT): This treatment employs cool (low energy) laser and a light-sensitive chemical- visudyne to destroy choroidal new blood vessels without damaging normal tissue. The PDT could not only limit vision loss in wet AMD but also significantly improve vision for 5.6% of cases ( gain 3 log lines or more ).
3. VEGF inhibitors: for wet
AMD. Currently, mainly 4 anti-VEGF
agents are available for clinical use:
- 1) Pegaptanib, approved by US FDA in 2004, is the first anti-VEGF agent for wet AMD . Its efficacy was demonstrated in the phase III clinical trial. 6 % of the patients in the treatment group gained 3 lines or more acuity as compared with 2 % in sham-injection group (GragoudasE S. 2004)
- 2) Ranibizumab( Lucentis), approved by US FDA in 2006, is the first treatment for neovascular AMD to improve vision for most patients (Rosenfield PJ,2006) . In the phase III clinical trial approximately 25-33 % of the patients treated with ranibizumab gained 3 lines or more in visual acuity, as compared with 5% or less in sham injection group at 12 and 24 months. ( Rosenfeld PJ,2006)<
- 3) Bevacizumab( Avastin) was approved by US FDA in 2004 for colorectal cancer treatment. However, given its lower cost, it has been widely used off-label for wet AMD in many countries. Its effectiveness was shown to be similar to that of Ranibizumab while Bevacizumab was linked to a higher risk of adverse events (Abouammoh M. 2011; The CATT group, 2011).
- 4) VEGF trap-eye( Eylea)was approved by US FDA in 2011 for wet AMD. The clinical trial results showed about 30% of the patients gained 3 lines or more in visual acuity during the study in both VEGF trap-eye group and the Ranibizumab group. Adverse effects also did not differ markedly between the two groups.( John Gever ,www.medpagetoday.com November 19,2011)
|
While the introduction of anti-VEGF agents into the treatment of wet MD is believed by Scientists and ophthalmologists a major advancement and a true revolution in the history of wet MD treatment (Bhisitjul, R B,2006; Waisbourd M, 2007; Schdmidt-ErfurthU, 2010), it is also important to know the shortcomings with these drugs :
- 1) These drugs have to be administered by intravitreous injections, which may cause severe complications;
- 2) The drugs themselves have some severe adverse effects;
- 3) These drugs are not effective for dry MD.
B. Chinese herbs for MD:
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) belongs to alternative medicine in the US medical system. And Chinese herb is an important part of TCM.
Modern pharmacology of Chinese herbs provides more detailed infomation regarding their exact effects on the body at organ, cell and molecular levels. These new knowledge may serve as an additional guide for herb selection and prescription on an evidence-oriented basis. Such a science-based herb combination would be able to target multiple controllable contributing factors and all kinds of pathologic changes accurately and comprehensively, and may, therefore, lead to a substantial increase in efficacy.
The following 6 unique features have been noticed with in the previous clinical observations:
- 1. Improving function (such as vision) not only for wet but also for dry MD, which is more common, but there is no effective western drug yet available.
- 2. May provide health benefits for MD of all kinds: Age-related, Myopic and Hereditary. Effective cases from each of the three types were observed in the past 14 years;
- 3. May benefit very severe AMD cases: Some individuals with so severe wet AMD that only a little vision left such as counting fingers at 15 cm in front of the eye (CF/15 cm). The eyes have been believed no hope to improve and no treatment was offered by previous doctors. But surprisingly, After taking Chinese herb extracts, their vision was improved to CF/40-300cm.
- 4. The herb extracts may benefit those AMD individuals who have previously received VEGF inhibitor injections. The benefits were exhibited in 3 ways: 1) Vision declined following the injections and then increased after taking herb extracts when the injection was discontinued. 2) Vision increased by the initial injections and then vision curve flattened; the increased vision either remained or fell slightly with subsequent injections. After discontinuation of the injection, the individuals started seeking alternative remedy and the vision further increased by herb extract intake which started 1-4 weeks after the last injection. 3) Vision improved significantly to like 20/20 after 3 consecutive monthly injections, which was, however, discontinued by the patient due to the fear of possible adverse events; then the vision was further improved to 20/13 -20/10 following herb intake and the increased macular thickness reduced accordingly. These further improvements have been kept for 14 months so far without additional injections. ( Note: the decision of no further injection was made by the retina specialist in charge after each follow-up examinations)
- 5. No severe adverse events like Endophthalmitis, Uveitis, Retinal tear, Vitreous hemorrhage, Lens Damage, Arterial hypertension, Myocardial infraction, and Stroke have ever been observed in the past 14 years; But slight elevation in intraocular pressure were encountered in the individuals who had a history of high or borderline IOP before.
- 6. The herbs are conveniently and safely administered by mouth and there is no cost for and complications from intraocular injections procedures.
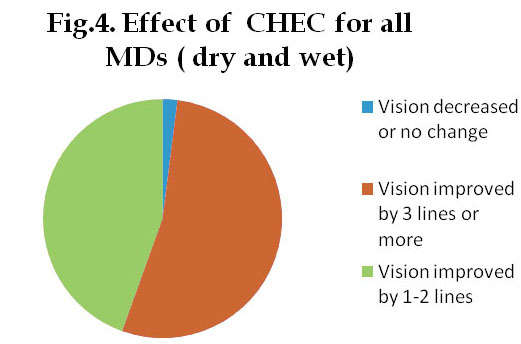
According to the previous uncontrolled clinical observations (before May 2011), the proportion of the eyes with vision improved by 3 log line or more were: 51.9% for all dry MDs, 56.3% for all wet MDs, 53,5% for all MDs (Fig. 4). The proportion of the eyes with vision improved by 1 log line or more among all dry and wet DMs was 98-100%. (These data were included in Wu's patent specification and published at USPTO official website (www.uspto.gov) on Nov. 08, 2012, Title: "Chinese herbal Composition for the Treatment of Macular Degeneration and the Process for Manufacturing the Same". Publication No: US-2012-02923330-A1; The data were also published by Chinese State Intellectual Property Office on September 21, 2011, with the same title in Chinese publication No: 102188637A).
|
Currently on US market, most dietary supplements for eyes claimed benefits for MD provide large amount of antioxidants among other nutrients. Antioxidants are important for fighting superoxidation, which is, however, only one of the 7 pathologic changes in the troubled macula. A most authoritative research, most notably the Age-Related Eye Disease study (AREDS), ( AREDS Report No. 22". Arch. Ophthalmol. 125 (9): 1225–32,2007.)concludes: Higher dietary intake of lutein/zeaxanthin was independently associated with decreased likelihood of having neovascular AMD( wet AMD), geographic atrophy( dry AMD), and large or extensive intermediate drusen. (SanGiovanni,JP et al, 2007). There is currently insufficient evidence to assess the effectiveness of dietary or supplemental antioxidants in treatment or primary prevention of ARMD.( Krishnadev N, Meleth AD, Chew EY (May 2010) "Nutritional supplements for age-related macular degeneration". Current Opinion in Ophthalmology 21 (3): 184–9. DOI:10.1097/ICU.0b013e32833866ee. PMC 2909501. PMID 20216418.
